Fluid-particle flows in fluidised beds and non-Newtonian media
Multiphase flows encompass a range of scales, such as flows of solids in gas or liquids in pneumatic conveying and fluidisations. Therefore, the behaviour of these systems needs to be well understood, for which it is important to predict the spatial distribution of the phases and measure the velocity profile, size distribution and volume fraction of the dispersed phase. In this case study, an optimised model will be developed to simulate the thermal-hydraulics of a fluidised bed reactor. The optimisation will be conducted to design and operate fluidised beds in nuclear reprocessing with a predictive tool for scaleup. Additionally, the diagnostic techniques will be improved (ultrasound and x rays) to verify if the operating conditions are close to expectations.
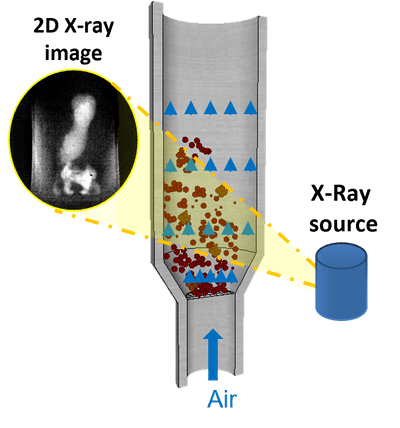
The experimental data on particle sizes, particle concentration, and interparticle interactions will be validated with the predictions from Lattice Boltzmann methods and used to build data-driven models. This will result in faster identification of the causes underlying deviation from optimal operating conditions in a nuclear reprocessing field.