Generative Adversarial Networks for COVID-19
This project consists of using a generative adversarial network (GAN) to predict the spatial variation of COVID-19 over time. GANs have been developed in the context of deep learning as a methodology to learn a representation of high-dimensional probability distribution from a given dataset. It comprises of two networks, a generator and a discriminator. The first one produces samples from the distribution learned, and the second one distinguishes between samples drawn from the training data and samples drawn from the generator. Therefore, a GAN will be trained to generate the spatial variation of the coronavirus infection over time. After training, we will perform a data assimilation to minimise the mismatch between the network predictions and the reference data.
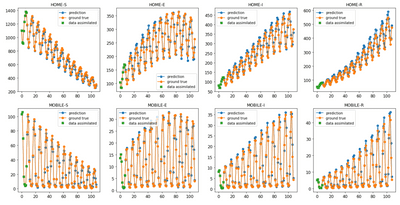
The figure shows the prediction of the outcomes of the spatial variation SEIR (Susceptible - Exposed - Infectious - Recovered ) model in one point of the mesh. The mesh can be seen as different locations in a city, country, or world. The simulation consists of two groups of people - people at home that cannot move and mobile people. Each cycle in the curves corresponds to a period of one day. GAN is capable of reasonably predicting the outcomes of the numerical model.